Page 38 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2021-digital
P. 38
of monitoring the surroundings on the
vehicle’s sensor suite. However, the shift
from Level 2 to Level 3 has been granular,
as the industry defined an intermediate
level called 2+. Level 2+ is empowered by
high-definition maps with foresight of the
horizon in both optimal and sub-optimal
driving conditions. Essentially, Level
2+ heightens a vehicle’s understanding
of its path, especially during absence of
lanes and unfamiliar driving destinations.
Beyond Level 3, ADAS Levels 4 and 5
will include autopilot (AP) on highways
and everywhere else, with high and full
automation capabilities that are a must for
robotic vehicles.
Most vehicles manufactured today
Figure 2: Light vehicle forecast and ADAS levels. SOURCES: Yole, IHS Markit are Level 0, however, it is expected
that the adoption of Level 1 and above
will increase as shown in Figure 2. For
example, in 2019 one in every six cars
sold was equipped with Level 2 and
above capability. However, towards the
end of the decade, nearly one in two
cars is expected to be at Level 2 and
above capability. The typical approach
of most OEMs has been to design Level
2 using multiple radar and camera
sensors. While this has been acceptable
so far, relying on just radar and camera
sensors may not be sufficient to enable
Level 3 and higher levels. Other sensors
such as LIDAR are gaining attention
because of their complementary nature
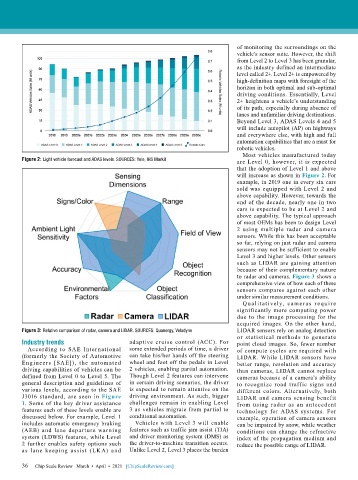
to radar and cameras. Figure 3 shows a
comprehensive view of how each of these
sensors compares against each other
under similar measurement conditions.
Qualit atively, cameras require
significantly more computing power
due to the image processing for the
acquired images. On the other hand,
Figure 3: Relative comparison of radar, camera and LIDAR. SOURCES: Quanergy, Velodyne LIDAR sensors rely on analog detection
or statistical methods to generate
Industry trends adaptive cruise control (ACC). For point cloud images. So, fewer number
According to SAE International some extended periods of time, a driver of compute cycles are required with
(formerly the Society of Automotive can take his/her hands off the steering LIDAR. While LIDAR sensors have
Engineers [SAE]), the automated wheel and foot off the pedals in Level better range, resolution and accuracy
driving capabilities of vehicles can be 2 vehicles, enabling partial automation. than cameras, LIDAR cannot replace
defined from Level 0 to Level 5. The Though Level 2 features can intervene cameras because of a camera’s ability
general description and guidelines of in certain driving scenarios, the driver to recognize road traffic signs and
various levels, according to the SAE is expected to remain attentive on the different colors. Alternatively, both
J3016 standard, are seen in Figure driving environment. As such, bigger LIDAR and camera sensing benefit
1. Some of the key driver assistance challenges remain in enabling Level from using radar as an antecedent
features each of these levels enable are 3 as vehicles migrate from partial to technology for ADAS systems. For
discussed below. For example, Level 1 conditional automation. example, operation of camera sensors
includes automatic emergency braking Vehicles with Level 3 will enable can be impaired by snow, while weather
(AEB) and lane departure warning features such as traffic jam assist (TJA) conditions can change the refractive
system (LDWS) features, while Level and driver monitoring system (DMS) as index of the propagation medium and
2 further enables safety options such the driver-to-machine transition occurs. reduce the possible range of LIDAR.
as lane keeping assist (LKA) and Unlike Level 2, Level 3 places the burden
36 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]
36