Page 11 - Chip Scale Review_March April_2022-digital
P. 11
Tech to further scale RDL dimensions
below 1µm using advances in SAP on
glass panels. Simultaneously, glass panel
packaging is also gaining momentum in
the industry with Asian and American
companies gearing up to manufacture
these latest panels, starting in 2022.
IC assembly reaches 10µm pitch
The need for smaller bump pitch has
led to continual progress in chip bonding
and assembly technologies as shown in
Figure 5. In the early years of packaging
– since the 1960s – wire bonding
provided the needed interconnections.
As the number of transistors grew on the
chip, flip-chip technology was developed
by IBM as an area array assembly
technology, initially at >200µm pitch,
and more recently to 100µm. As solder
bridging began to occur between
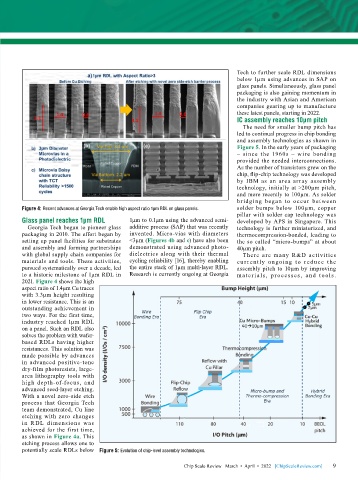
Figure 4: Recent advances at Georgia Tech enable high aspect ratio 1µm RDL on glass panels. solder bumps below 100µm, copper
pillar with solder cap technology was
Glass panel reaches 1µm RDL 1µm to 0.1µm using the advanced semi- developed by APS in Singapore. This
Georgia Tech began to pioneer glass additive process (SAP) that was recently technology is further miniaturized, and
packaging in 2010. The effort began by invented. Micro-vias with diameters thermocompression-bonded, leading to
setting up panel facilities for substrates <3µm (Figures 4b and c) have also been the so called “micro-bumps” at about
and assembly and forming partnerships demonstrated using advanced photo- 40µm pitch.
with global supply chain companies for dielectrics along with their thermal There are many R&D activities
materials and tools. These activities, cycling reliability [16], thereby enabling cu r rently ongoi ng to reduce t he
pursued systematically over a decade, led the entire stack of 1µm multi-layer RDL. assembly pitch to 10µm by improving
to a historic milestone of 1µm RDL in Research is currently ongoing at Georgia mater ials, processes, a nd tools.
2021. Figure 4 shows the high
aspect ratio of 1.4µm Cu traces
with 3.3µm height resulting
in lower resistance. This is an
outstanding achievement in
two ways. For the first time,
industry reached 1µm RDL
on a panel. Such an RDL also
solves the problem with wafer-
based RDLs having higher
resistances. This solution was
made possible by advances
in advanced positive-tone
dry-film photoresists, large-
area lithography tools with
high depth-of-focus, and
advanced seed-layer etching.
With a novel zero-side etch
process that Georgia Tech
team demonstrated, Cu line
etching with zero changes
in R DL dimensions was
achieved for the first time,
as shown in Figure 4a. This
etching process allows one to
potentially scale RDLs below Figure 5: Evolution of chip-level assembly technologies.
Chip Scale Review March • April • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 9 9