Page 46 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 46
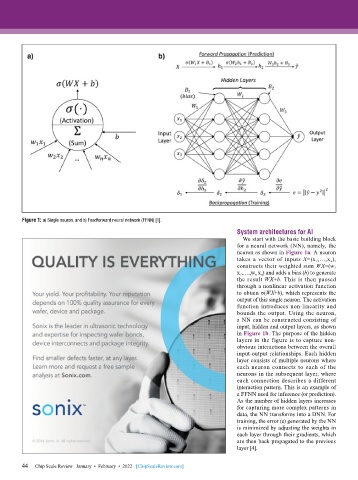
Figure 1: a) Single neuron, and b) Feedforward neural network (FFNN) [1].
System architectures for AI
We start with the basic building block
for a neural network (NN), namely, the
neuron as shown in Figure 1a. A neuron
takes a vector of inputs X=(x 1 ,…,x n ),
constructs their weighted sum WX=(w 1
x 1 ,….,w n x n ) and adds a bias (b) to generate
the result WX+b. This is then passed
through a nonlinear activation function
to obtain σ(WX+b), which represents the
output of this single neuron. The activation
function introduces non-linearity and
bounds the output. Using the neuron,
a NN can be constructed consisting of
input, hidden and output layers, as shown
in Figure 1b. The purpose of the hidden
layers in the figure is to capture non-
obvious interactions between the overall
input-output relationships. Each hidden
layer consists of multiple neurons where
each neuron connects to each of the
neurons in the subsequent layer, where
each connection describes a different
interaction pattern. This is an example of
a FFNN used for inference (or prediction).
As the number of hidden layers increases
for capturing more complex patterns in
data, the NN transforms into a DNN. For
training, the error (e) generated by the NN
is minimized by adjusting the weights in
each layer through their gradients, which
are then back propagated to the previous
layer [4].
44 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]
44