Page 29 - Chip Scale Review_Jul Aug_2022-digital
P. 29
validation to be performed on a complete
probe head + PCB assembly, using a probe
card analyzer. A design of experiments
(DOE) has been defined to assess the
variability of the manufacturing processes,
using several copies of the probe heads and
PCBs, which are manufactured at different
times and will be assembled and tested in
different combinations.
More efficient multi-site layout
For high-volume production test, a more
compact multi-site layout is preferred, as
it will typically result in fewer skipped die
when testing near the edge of the wafer,
thereby translating into higher overall
touchdown efficiency, higher throughput,
and therefore, a lower cost of test (COT).
The original test site layout implemented 8
sites in a 1x8 single row, with three skipped
die between each site. This was required to
accommodate the large amount of RF test
circuitry routed out from each site.
A new design has been proposed that
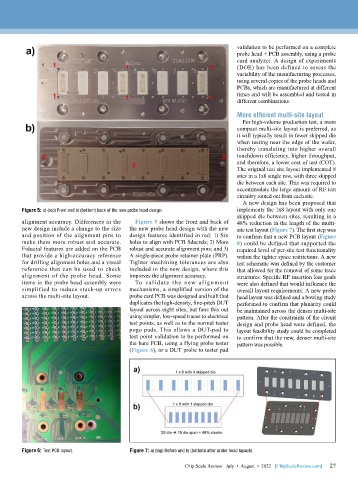
Figure 5: a) (top) Front and b) (bottom) back of the new probe head design. implements the 1x8 layout with only one
skipped die between sites, resulting in a
alignment accuracy. Differences in the Figure 5 shows the front and back of 48% reduction in the length of the multi-
new design include a change to the size the new probe head design with the new site test layout (Figure 7). The first step was
and position of the alignment pins to design features identified in red: 1) Six to confirm that a new PCB layout (Figure
make them more robust and accurate. holes to align with PCB fiducials; 2) More 8) could be defined that supported the
Fiducial features are added on the PCB robust and accurate alignment pins; and 3) required level of per-site test functionality
that provide a high-accuracy reference A single-piece probe retainer plate (PRP). within the tighter space restrictions. A new
for drilling alignment holes and a visual Tighter machining tolerances are also test schematic was defined by the customer
reference that can be used to check included in the new design, where this that allowed for the removal of some trace
alignment of the probe head. Some improves the alignment accuracy. structures. Specific RF insertion loss goals
items in the probe head assembly were To validate the new alig n ment were also defined that would influence the
simplified to reduce stack-up errors mechanisms, a simplified version of the overall layout requirements. A new probe
across the multi-site layout. probe card PCB was designed and built that head layout was defined and a bowing study
duplicates the high-density, fine-pitch DUT performed to confirm that planarity could
layout across eight sites, but fans this out be maintained across the denser multi-site
using simpler, low-speed traces to electrical pattern. After the constraints of the circuit
test points, as well as to the normal tester design and probe head were defined, the
pogo pads. This allows a DUT-pad to layout feasibility study could be completed
test point validation to be performed on to confirm that the new, denser multi-site
the bare PCB, using a flying probe tester pattern was possible.
(Figure 6), or a DUT probe to tester pad
Figure 6: Test PCB layout. Figure 7: a) (top) Before and b) (bottom) after probe head layouts.
27
Chip Scale Review July • August • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 27