Page 52 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 52
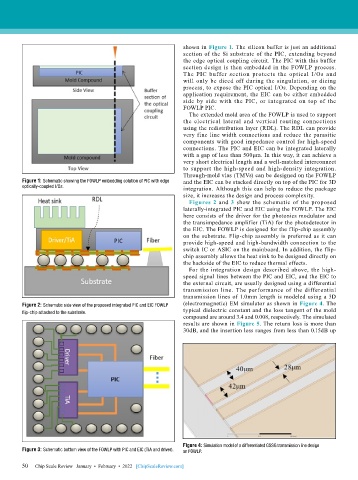
shown in Figure 1. The silicon buffer is just an additional
section of the Si substrate of the PIC, extending beyond
the edge optical coupling circuit. The PIC with this buffer
section design is then embedded in the FOWLP process.
The PIC buffer section protects the optical I/Os and
will only be diced off during the singulation, or dicing
process, to expose the PIC optical I/Os. Depending on the
application requirement, the EIC can be either embedded
side by side with the PIC, or integrated on top of the
FOWLP PIC.
The extended mold area of the FOWLP is used to support
the electrical lateral and vertical routing connections
using the redistribution layer (RDL). The RDL can provide
very fine line width connections and reduce the parasitic
components with good impedance control for high-speed
connections. The PIC and EIC can be integrated laterally
with a gap of less than 500μm. In this way, it can achieve a
very short electrical length and a well-matched interconnect
to support the high-speed and high-density integration.
Through-mold vias (TMVs) can be designed on the FOWLP
Figure 1: Schematic showing the FOWLP embedding solution of PIC with edge and the EIC can be stacked directly on top of the PIC for 3D
optically-coupled I/Os. integration. Although this can help to reduce the package
size, it increases the design and process complexity.
Figures 2 and 3 show the schematic of the proposed
laterally-integrated PIC and EIC using the FOWLP. The EIC
here consists of the driver for the photonics modulator and
the transimpedance amplifier (TiA) for the photodetector in
the EIC. The FOWLP is designed for the flip-chip assembly
on the substrate. Flip-chip assembly is preferred as it can
provide high-speed and high-bandwidth connection to the
switch IC or ASIC on the mainboard. In addition, the flip-
chip assembly allows the heat sink to be designed directly on
the backside of the EIC to reduce thermal effects.
For the integration design described above, the high-
speed signal lines between the PIC and EIC, and the EIC to
the external circuit, are usually designed using a differential
transmission line. The performance of the differential
transmission lines of 1.0mm length is modeled using a 3D
Figure 2: Schematic side view of the proposed integrated PIC and EIC FOWLP (electromagnetic) EM simulator as shown in Figure 4. The
flip-chip attached to the substrate. typical dielectric constant and the loss tangent of the mold
compound are around 3.4 and 0.008, respectively. The simulated
results are shown in Figure 5. The return loss is more than
30dB, and the insertion loss ranges from less than 0.15dB up
Figure 4: Simulation model of a differentiated GSSG transmission line design
Figure 3: Schematic bottom view of the FOWLP with PIC and EIC (TiA and driver). on FOWLP.
50 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]
50