Page 32 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 32
Managing trade-offs in the chiplet era
By Rob Munoz [Intel]
I n his famous 1965 paper [1]
Gordon Moore foreshadowed that
a chiplet-like approach would
become attractive. By chiplets, we mean
die that have been optimized to connect
to other die within the same packaged
device. Intel has used the term “tiles”
to describe chiplets that are integrated
using high-density, high-bandwidth
interconnects enabled by advanced
packaging technologies such as Intel’s
2.5D embedded multi-die interconnect
bridge (EMIB) [2], 3D Foveros [3], and
combined EMIB-Foveros (Co-EMIB)
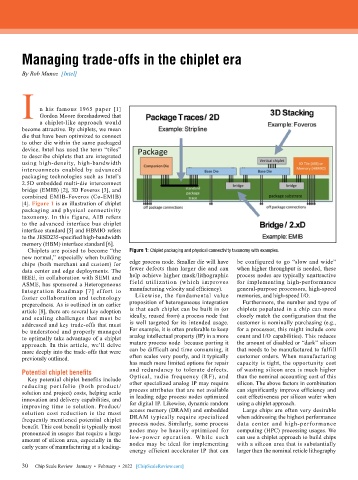
[4]. Figure 1 is an illustration of chiplet
packaging and physical connectivity
taxonomy. In this figure, AIB refers
to the advanced interface bus chiplet
interface standard [5] and HBMIO refers
to the JESD235-specified high-bandwidth
memory (HBM) interface standard [6].
Chiplets are poised to become “the Figure 1: Chiplet packaging and physical connectivity taxonomy with examples.
new normal,” especially when building
chips (both merchant and custom) for edge process node. Smaller die will have be configured to go “slow and wide”
data center and edge deployments. The fewer defects than larger die and can when higher throughput is needed, these
IEEE, in collaboration with SEMI and help achieve higher mask/lithographic process nodes are typically unattractive
ASME, has sponsored a Heterogeneous f ield utilization (which improves for implementing high-performance
Integration Roadmap [7] effort to manufacturing velocity and efficiency). general-purpose processors, high-speed
foster collaboration and technology Likewise, the fundamental value memories, and high-speed I/O.
preparedness. As is outlined in an earlier proposition of heterogeneous integration Furthermore, the number and type of
article [8], there are several key adoption is that each chiplet can be built in (or chiplets populated in a chip can more
and scaling challenges that must be ideally, reused from) a process node that closely match the configuration that the
addressed and key trade-offs that must is well targeted for its intended usage. customer is nominally purchasing (e.g.,
be understood and properly managed For example, it is often preferable to keep for a processor, this might include core
to optimally take advantage of a chiplet analog intellectual property (IP) in a more count and I/O capabilities). This reduces
approach. In this article, we’ll delve mature process node because porting it the amount of disabled or “dark” silicon
more deeply into the trade-offs that were can be difficult and time consuming, it that needs to be manufactured to fulfill
previously outlined. often scales very poorly, and it typically customer orders. When manufacturing
has much more limited options for repair capacity is tight, the opportunity cost
Potential chiplet benefits and redundancy to tolerate defects. of wasting silicon area is much higher
Key potential chiplet benefits include Optical, radio frequency (RF), and than the nominal accounting cost of this
reducing portfolio (both product/ other specialized analog IP may require silicon. The above factors in combination
solution and project) costs, helping scale process attributes that are not available can significantly improve efficiency and
innovation and delivery capabilities, and in leading edge process nodes optimized cost effectiveness per silicon wafer when
improving time to solution. Product/ for digital IP. Likewise, dynamic random using a chiplet approach.
solution cost reduction is the most access memory (DRAM) and embedded Large chips are often very desirable
frequently mentioned potential chiplet DRAM typically require specialized when addressing the highest performance
benefit. This cost benefit is typically most process nodes. Similarly, some process data center and high-performance
pronounced in usages that require a large nodes may be heavily optimized for computing (HPC) processing usages. We
amount of silicon area, especially in the low-power operation. While such can use a chiplet approach to build chips
early years of manufacturing at a leading- nodes may be ideal for implementing with a silicon area that is substantially
energy efficient accelerator IP that can larger than the nominal reticle lithography
30
30 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]