Page 47 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2023-digital
P. 47
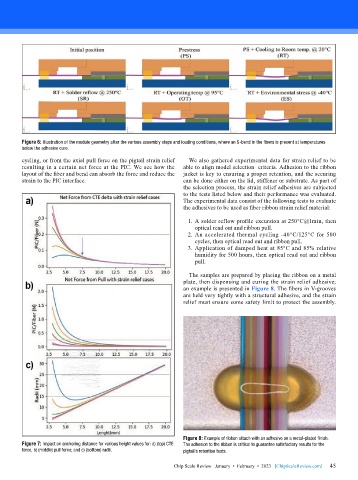
Figure 6: Illustration of the module geometry after the various assembly steps and loading conditions, where an S-bend in the fibers is present at temperatures
below the adhesive cure.
cycling, or from the axial pull force on the pigtail strain relief We also gathered experimental data for strain relief to be
resulting in a certain net force at the PIC. We see how the able to align model selection criteria. Adhesion to the ribbon
layout of the fiber and bend can absorb the force and reduce the jacket is key to ensuring a proper retention, and the securing
strain to the PIC interface. can be done either on the lid, stiffener or substrate. As part of
the selection process, the strain relief adhesives are subjected
to the tests listed below and their performance was evaluated.
The experimental data consist of the following tests to evaluate
the adhesives to be used as fiber ribbon strain relief material:
1. A solder reflow profile excursion at 250°C@1min, then
optical read out and ribbon pull.
2. An accelerated thermal cycling -40°C/125°C for 500
cycles, then optical read out and ribbon pull.
3. Application of damped heat at 85°C and 85% relative
humidity for 500 hours, then optical read out and ribbon
pull.
The samples are prepared by placing the ribbon on a metal
plate, then dispensing and curing the strain relief adhesive;
an example is presented in Figure 8. The fibers in V-grooves
are held very tightly with a structural adhesive, and the strain
relief must ensure some safety limit to protect the assembly.
Figure 8: Example of ribbon attach with an adhesive on a metal-plated finish.
Figure 7: Impact on anchoring distance for various height values for: a) (top) CTE The adhesion to the ribbon is critical to guarantee satisfactory results for the
force, b) (middle) pull force; and c) (bottom) radii. pigtail’s retention tests.
45
Chip Scale Review January • February • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 45